Some pundits are sounding the alarm that the Ebola epidemic could destabilize West Africa politically and economically possible giving an opening for extremists to gain control of the countries in the region.

(John Moore/Getty Images)
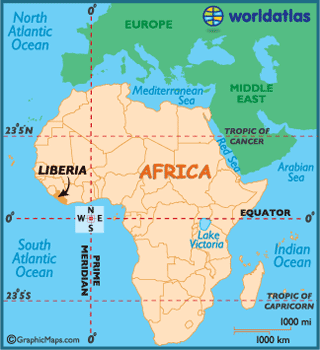
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country in West Africa bordered by Sierra Leone to its west, Guinea to its north and Ivory Coast to its east.
Liberia is the only country in Africa founded by United States colonization while occupied by native Africans. Beginning in 1820, the region was colonized by African Americans, most of whom were freed slaves.
The colonizers (who later become known as Americo-Liberians) established a new country with the help of the American Colonization Society, a private organization whose leaders thought former slaves would have greater opportunity in Africa.
African captives freed from slave ships by the British and Americans were sent there instead of being repatriated to their countries of origin.
In 1847, this new country became the Republic of Liberia, establishing a government modeled on that of the United States and naming its capital city Monrovia after James Monroe, the fifth president of the United States and a prominent supporter of the colonization. The colonists and their descendants, known as Americo-Liberians, led the political, social, cultural and economic sectors of the country and ruled the nation for over 130 years as a dominant minority.
The country began to modernize in the 1940s following investment by the United States during World War II and economic liberalization under President William Tubman.
Liberia was a founding member of the United Nations and the Organisation of African Unity.
1980 a military coup overthrew the Americo-Liberian leadership, marking the beginning of political and economic instability and two successive civil wars. These resulted in the deaths of between 250,000 and 520,000 people and devastated the country's economy.
A peace agreement in 2003 led to democratic elections in 2005.
Today, Liberia is recovering from the lingering effects of the civil wars and their consequent economic upheaval, but about 85% of the population continue to live below the international poverty line, and the country's economic and political stability has recently been threatened by a deadly Ebola virus epidemic.
Liberia - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia:
Link: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liberia
'via Blog this'
No comments:
Post a Comment